Temperature Mapping
Temperature mapping is the mapping of spatial temperature distribution within a certain volume, and in the life sciences field it targets refrigerators, freezers, incubators, thermostatic chambers, pharmaceutical warehouses, transport storage equipment, etc. used to store pharmaceuticals and other products. However, equipment such as refrigerators, freezers, incubators, and thermostatic chambers are often referred to as temperature distribution tests, and in Japan temperature mapping tends to target relatively large facilities and equipment such as pharmaceutical warehouses, refrigerated warehouses, and transport storage equipment.
Temperature Mapping Leaflet
Purpose of Temperature Mapping
The environment in which pharmaceuticals are stored and transported is important, and temperature mapping is performed as one of the validation items for pharmaceutical warehouses, vehicles, and containers. For newly constructed pharmaceutical warehouses and cold storage warehouses, performance evaluation is performed during no-load (nothing inside the warehouse) operation as operational qualification (OQ) for warehouse validation. For existing pharmaceutical warehouses and cold storage warehouses, temperature mapping may be performed in summer and winter under load (normal storage conditions) as performance qualification (PQ). In addition to evaluating the temperature in the storage space, temperature mapping also aims to find the worst points (high temperature/low temperature) to determine the sensor positions for temperature monitoring.
There are also opinions that regular temperature mapping is necessary due to factors such as recent climate change and deterioration of air conditioning equipment.
Temperature Mapping Regulations
On December 28, 2018, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare officially issued GDP guidelines in Japan as an administrative notice titled "
Guidelines for Good Distribution Practice (GDP) of Pharmaceuticals." The contents are in accordance with the GDP of PIC/S (Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention and Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme). It clearly states that "temperature mapping should be carried out under appropriate conditions before using the storage area," and "when using vehicles with temperature control devices, temperature mapping should be carried out under representative conditions and seasonal fluctuation factors should be taken into consideration if necessary."
There are also related regulations regarding temperature mapping overseas. For example, the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USPC) published "usp36 1079 Good Storage and Distribution Practices For Drug Products" describes factors to be considered when mapping facilities and dedicated containers/vehicles. In addition, the WHO's "Temperature mapping of storage areas" Chapter 2 Guidance, 2.2 The mapping protocol, describes the following items regarding mapping.
- Approval page and change management history
- Abbreviations and Glossary
- Explanation and justification
- range
- the purpose
- Methodology
- Mapping Report Template
- Includes a template for the mapping report and, where appropriate, annexes
Conducting temperature mapping
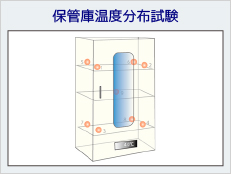
When implementing temperature mapping in a pharmaceutical warehouse, the problem is the diversity of warehouse environments. For equipment such as refrigerators, freezers, incubators, and thermostatic baths, the measurement points for measuring temperature distribution are determined by their volume, but in the case of warehouses, there are a wide range of factors to consider, such as the controlled temperature range, the wide range of volume (from extra-large to small rooms), the presence and placement of shelves and racks, the effects of product characteristic, the effects of the positions of air conditioners and air control sensors, the frequency of people entering and exiting the warehouse, the number of doors and windows, and the effects of the seasons and outside temperatures.
When implementing warehouse temperature mapping in practice, the following points need to be considered:
- Position and number of measurement points (spacing, height)
- Measurement period, measurement interval
- Measurement methods (normal operation, operation during power outage, door open, emergency operation)
- Measurement period (summer, winter)
- Measuring Instrument Type
Temperature mapping is usually carried out as part of warehouse validation, so temperature mapping also follows the same process as validation methods: create a plan → implement → write a report → approve.
Our Response
We have sensors and measuring equipment suitable for temperature mapping and provide calibration services, but we also undertake temperature and humidity mapping work. In particular, we have many high accuracy wireless loggers for temperature mapping, which allows us to accurately measure the temperature mapping of large spaces or multiple warehouses in a short period of time.
In addition, the measuring instrument uses a system that complies with FDA 21CFR Part 11, so data can be treated as reliable electronic records.
In principle, temperature mapping is carried out in accordance with validation methods, so we can respond to customer requests regarding plans, implementation methods, reports, etc.
There are various implementations of temperature mapping due to the diversity of warehouse environments, so please feel free to contact us if you are considering temperature mapping.
Temperature Mapping Examples
Compatible Products

Real-time wireless logger MZ (Japan Only)
configuration of a wireless logger that measures temperature, a receiver equipped with various interface communications and GPS, and application software.
Compatible with mobile devices, and can be operated without a computer depending on the purpose
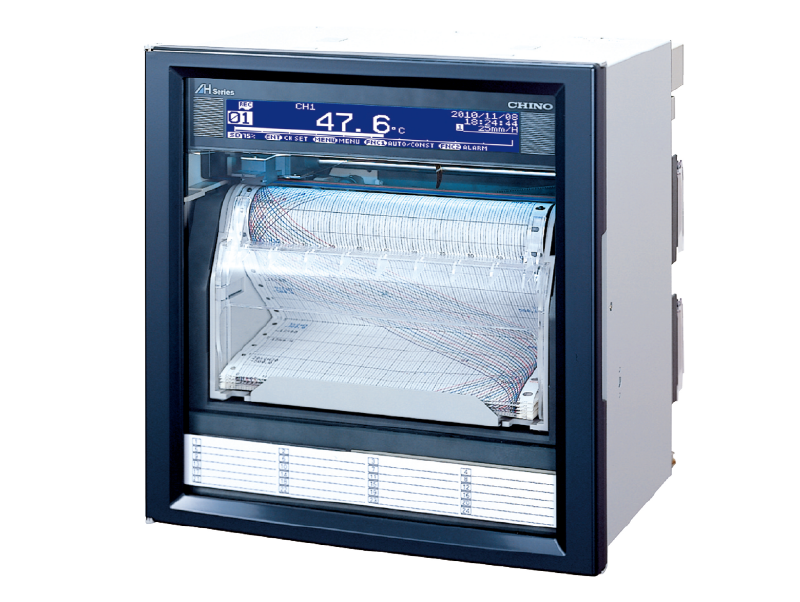

hybrid Memory recorder AH4000 Series (dot printing type Type)
This hybrid recorder has a recording width of 180 mm and is available in 6-point, 12-point, and 24-point input dot printing type-printing models. Data can be recorded not only to chart but also to an SD card at the same time, and the saved data can be replay and analyzing on a PC.